To pass the metallic pipe era, it’s required to bring in brand-new choices that beat metal ones by their superior characteristics. At that time, RTR pipes came into the game to replace corrosion-free, lightweight, and durable pipelines when needed. GRP, GRV, and GRE pipes are such strong and reliable examples of RTR pipes in oil and gas, water systems, and chemical plants in industrial use cases.
Then let’s dive into the RTR family and its substances to figure out how these pipes can last over decades with no leak or crack. Keep reading from types and material compositions to the manufacturing and installation process.
Before getting into the main blog text, check the infographic below to understand how RTR pipes are divided into GRP, GRV, and GRE pipes:
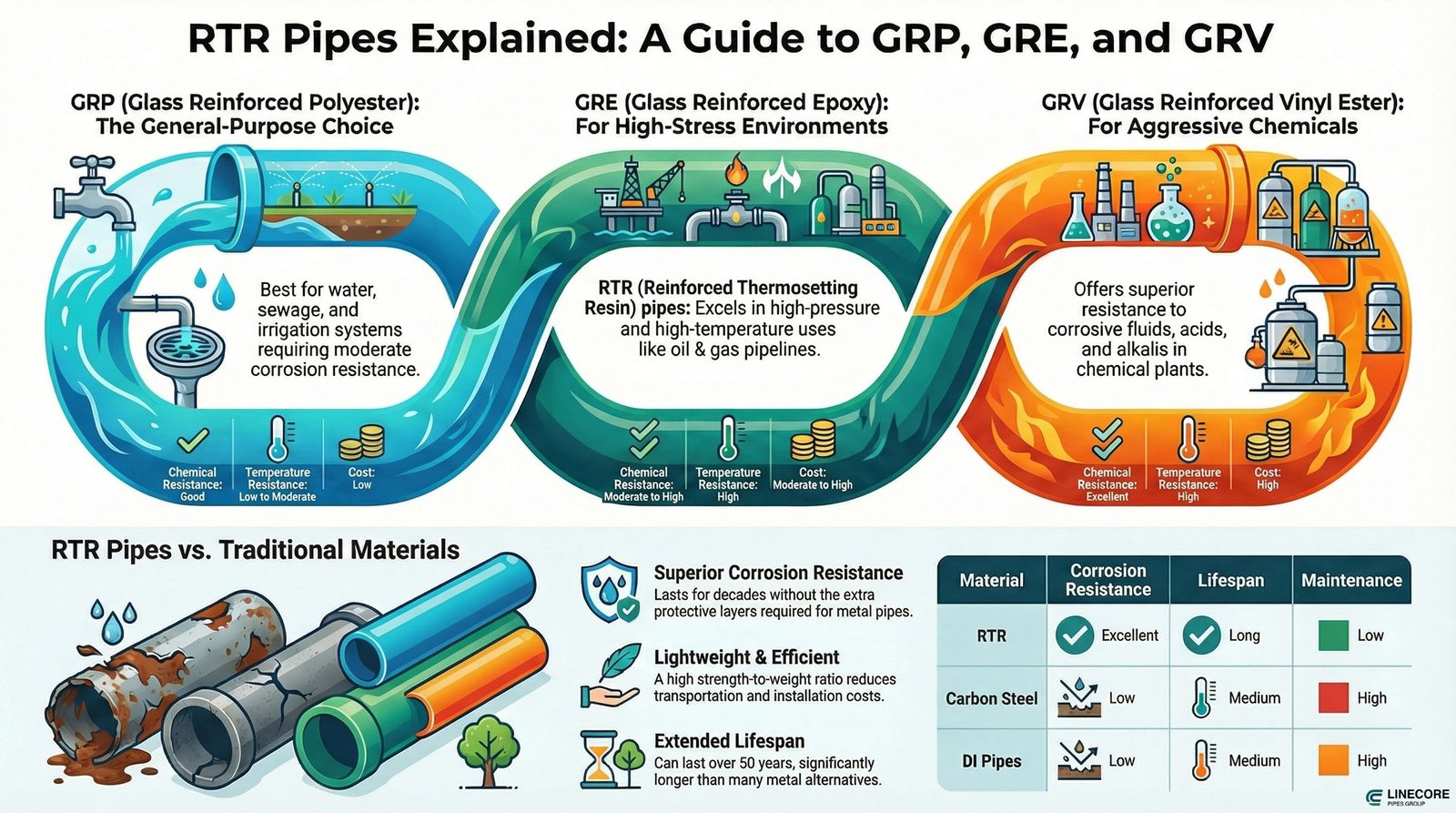
RTR pipes infographic (Source: Pipelinecoregroup.com)
Terminology & Types of RTR Pipes
RTR (Reinforced Thermosetting Resin) pipes are made of thermosetting resin such as polyester, vinyl ester, or epoxy, each of which can improve specific properties like resistance to chemicals or high temperatures in oil and gas or chemical plants.
Industry Terms and Synonyms for RTR Pipes
Here is what RTR pipes mean in the industrial environment:
- RTRP (Reinforced Thermosetting Resin Pipes)
- FRP (Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic)
- GRP (Glass Reinforced Polyester)
- GRE (Glass Reinforced Epoxy
- GRV (Glass Reinforced Vinyl Ester)
These terms can refer to different types of RTR pipes that are used in their own special applications, from urban systems to industrial plants.
What Are the Differences between GRP, GRV, and GRE Pipes?
The resin type used in each of GRP, GRV, or GRE pipes indicates how they’ll behave under heavy loads and harsh conditions. Besides the brief explanation, check the table below that points out this matter:
- GRP (Glass Reinforced Polyester): These pipes are made of glass fibers and unsaturated polyester resin, which are mainly used in water infrastructure and more general use cases like water supply in cities that require medium resistance to corrosion.
- GRE (Glass Reinforced Epoxy): GRE pipes replace epoxy resin with polyester to improve characteristics like strength, flexibility, and higher resistance to temperature in extreme conditions like firewater plants or oil and gas systems that require both pressure and thermal toleration.
- GRV (Glass Reinforced Vinyl Ester): These pipes are also made of glass fibers, but the resin type is vinyl ester, which helps pipes to resist corrosive soils or aggressive chemicals like acids and alkalis.
| Property | GRP (Glass Reinforced Polyester) | GRE (Glass Reinforced Epoxy) | GRV (Glass Reinforced Vinyl Ester) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resin Type | Polyester | Epoxy | Vinyl Ester |
| Strength | Moderate | High | Very High |
| Temperature Resistance | Low to Moderate | High | High |
| Chemical Resistance | Good | Moderate to High | Excellent |
| Common Applications | Water, Sewage, Irrigation | Offshore, High-Pressure Flowlines | Chemical Processing, Acid Transport |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good | Very Good | Superior |
| Cost | Low | Moderate to High | High |
| Flexibility | Moderate | High | Moderate |
When to Use Each Type Based on Application
Choose GRP pipe for low-pressure and non-corrosive use cases like water supply and sewage systems.
GRE pipes are popularly used in high-pressure and high-temperature, offshore, and oil and gas pipelines due to their rich epoxy resin base.
Lastly, choose GRV pipes in chemical processing or desalination plants where marine or aggressive fluids require high corrosion resistance.
Material Compositions of RTR Pipes: What Exactly Are GRP, GRV, and GRE Pipes Made of?
The material composition of RTR pipes shows how they’ll react in certain conditions. From fibers to resin matrix and additives, all have their specific impact on the final product. Let’s break them into pieces in this section:
1. Thermosetting Resins
The case of resin types in RTR pipes is clearer than other use cases; this matter refers to the ability of resin to keep the pipes safe under aggressive conditions.
- Polyester Resin: Used for more general use cases where the average rating of corrosion resistance and low-temperature services like water supply or sewage systems has the least requirements for extra resin coatings. (Source: Research Publish Journals)
- Epoxy Resin: Epoxy resin matrix is known as a great coating for aggressive and extreme thermal conditions, like oil and gas and offshore pipelines. This resin choice can prevent damage from both high temperatures and harsh, corrosive environments.
- Vinyl Ester Resin: Used to achieve the best corrosion resistance among these three resin bases. In industrial use cases like chemical processing, where aggressive fluids like acids and alkalis require such strong and durable pipelines as GRV pipes.
2. Glass Fiber Reinforcement
E-glass: E-glass is the most commonly used glass fiber in the structural layer, which indicates how the pipe will act under heavy loads. It provides good mechanical properties and is used in most general-purpose RTR pipes for standard structural reinforcement.
C-glass: Known for its chemical barrier properties, C-glass fibers offer excellent resistance to acidic and alkaline environments. It’s commonly used in applications where chemical exposure is a concern.
ECR-glass: As noted in Amiblu, ECR-glass (Electrical and Chemical Resistance glass) is designed for applications where electrical or chemical resistance is needed and is perfectly used for environments with high electrical conductivity.
3. Additives and Fillers
In the case of additives, we face multiple choices, each of which has an impact on a specific characteristic of RTR pipes. Check the table below for more information on GRP family filers and additives.
| Additive/Filler | Function | Specific Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Flame Retardants | Reduces flammability | Firewater systems and offshore piping |
| Curing Agents | Hardens resin | GRE and GRP pipes in water injection |
| Catalysts | Speeds up curing process | GRE pipes for high-pressure flowlines |
| Siliceous Sand Fillers | Increases strength and stiffness | GRP pipes for municipal water systems |
| UV Stabilizers | Protects against UV degradation | GRP pipes in outdoor water pipelines |
| Antioxidants | Prevents resin degradation | RTR pipes in offshore platforms |
| Colorants/Dyes | Adds color for identification | FRP pipes in chemical plants |
| Plasticizers | Increases flexibility | GRP pipes in tight-radius bends |
| Accelerators | Speeds up polymerization | GRE pipes for offshore oil pipelines |
RTR Pipes Manufacturing Process & Techniques
RTR pipes and more detailed GRP pipes can be produced by several methods, such as filament winding, pultrusion, hand lay-up, and centrifugal casting, each of which may be used to add certain properties to the final product.
Filament Winding
The most used method for making RTR pipes is to create pipes by adding continuous glass fibers and resin through a mandrel to shape pipes to various designs and directions.
- Axial, hoop, or helical oriented pipes can be made via this technique, which results in durable pipes with a high rate of stiffness under external loads. (Source: Scribd)
- This technique is perfect for high-pressure and large-diameter designs.
Centrifugal Casting
The second case of RTR manufacturing processes starts with glass fiber preparation (impregnation by resin). A rotating mold in this step helps pipes to get the piping shape in smooth and uniform structures.
- This method makes a smooth internal surface for GRP pipes to speed up the flow rate.
- In small to medium diameters, centrifugal casting controls the correctness of the pipe’s design.
Hand Lay-up
Got to the special shape of RTR pipes? Hand lay-up is what you should choose, which involves laying resin and glass fibers and then adding resin to these layers by spraying or brushing.
- This process requires well-rounded workers to shape the pipes correctly on a smaller scale.
- This method can make special pieces for fitting and joints as well.
Pultrusion
The pultrusion method is barely used compared to other methods. This process uses glass fibers that have gone through a resin bath and are pulled to shape like a pipe.
- Tip: In a pipe with a long length, pultrusion makes the wall thickness the same all over the pipe’s body. (ScienceDirect)
The Curation of Resin and the Polymerization Process
Once the resin is added to glass fibers, it’s time to let it cure. Here’s how this process goes:
There are specific temperatures (room temp or 40°C for the pre-curing process, for instance) and for the main process of each resin type, a different temperature. (The table below shows these specific temperatures.)
| Resin Type | Curing Temperature Range |
|---|---|
| Polyester Resin | 60°C to 80°C (140°F to 176°F) |
| Epoxy Resin | 80°C to 120°C (176°F to 248°F) |
| Vinyl Ester Resin | 70°C to 100°C (158°F to 212°F) |
| Low-Temperature Resins | 40°C to 60°C (104°F to 140°F) |
Adding catalysts can speed up the curing process, which improves some of their mechanical features as well.
Specifications and Standards for RTR Pipes
RTR pipes require global standards and guidelines to follow and be allowed to create that durable infrastructure for cities and industrial areas. Check specifications below and their standards suggested to get verified by:
Diameter Range: DN25 to DN1200 (1” to 48”)
Pressure Class: Up to 3000 psi (20–210 bar)
Temperature Class: Indicated by a range of -40°C to +120°C
Wall Thickness & Stiffness Classes: Pipes are rated according to SN ratings to define their stiffness and durability under load.
| Standard | Description |
|---|---|
| ISO 14692 | Composite pipes for oil & gas |
| API 15HR | High-pressure GRE pipes |
| API 15LR | Low-pressure GRE pipes |
| ASTM D2310 | Glass fiber pipes for pressure |
| ASTM D3262 | FRP pipes for drainage |
| BS EN 1796 | FRP pipes for buried systems |
| ISO 9046 | GRP pipes for water treatment |
These standards help engineers choose a reliable pipeline that is adapted to worldwide piping system use.
Jointing Methods of RTR Pipes
The way RTR pipes are connected shows how leakproof they’ll be in their long-lasting lifetime. Here are the most-used methods based on two restrained and unrestrained categories.
Restrained Joints
Restrained joints are such connections that include no change or movement in joints where the pressure of both fluids and external loads is high. Here are some popular types:
- Bell and Spigot: This system uses adhesives and epoxy to seal the connection of bell and spigot for good in high-pressure systems.
- Butt-And-Wrap Lamination: To make this type, according to Scribd, laminated glass fibers are rounded around the joint area to create a leak-free connection in permanent joints.
- Threaded Couplings: This type is used less than the others, though it is used when a smaller connection in more sensitive areas is required as an easy and ready-to-apply jointing method.
Unrestrained Joints
In the case of unrestrained joints that are more flexible and changeable with gaskets or mechanical couplings, in places where easy-to-install joints are needed.
- Rubber Gasketed Joints: To shape the connection between two pipe ends, a rubber gasket allows pipes to act more flexibly, unlike the restrained joints.
- Mechanical Couplings: Via using bolts or mechanical features, connect pipes in sites where the speed of installation matters the most.
- Flanged Connections: The easiest way to connect two RTR pipes is by bolted flanges for both high- and low-pressure systems in hard-to-access locations.
What Are the Best Practices for Joining the RTR Pipes across Various Use Cases?
To achieve reliability in the long-term performance of RTR pipes, use heating blankets that control the curing process of resin in the installation procedure.
Also, be careful about the points below to make a connection with no leakage included:
- Clean pipe ends.
- Cure resin properly.
- Inspect for leaks.
Don’t forget to check gaps and the right tolerance to avoid any probable misalignment.
How To Store, Transport, And Handle RTR Pipes Properly?
Once the pipes are ready to store, be careful about how you store them to avoid any possible cracks or deformation. Use wooden beams to place them at a distance and prevent misalignments. Also, check the tips below to transport them correctly to the installation area.
UV Protection
When you’re storing RTR pipes, they may be placed under the UV light, and as not all of them are resistant to this light, they may not survive. Then check the resin type used in the coating and place pipes correctly with UV-protective shields.
Use of Nylon Slings
In the handling and transportation process, use nylon slings instead of metal chains that may damage pipes on the surface.
Adhesive Temperature Control
To cure adhesives properly, the temperature must not be too cold or too hot, as this may make the joints weak.
Marking Pipes
To track them easily after the installation or for further maintenance, mark pipes with clear information to make the QC process easier.
What Are the Applications of RTR Pipes?
RTR pipes include beneficial characteristics that make them fit in various applications from offshore to chemical processing in industrial environments.
- Oil & Gas Operations: RTR pipes are the best option among modern solutions for flowlines. Also, water injection systems that require corrosion and high-pressure resistance are able to choose GRE pipes in marine conditions or fire-retardant GRE pipes under extreme temperatures.
- Seawater and Brine Handling: In these systems, RTR pipes can be used due to their easy handling and lightweight in desalination plants with no corrosion issues. GRV pipes are the top choices for marine conditions, and more specifically, in saline water.
- Firewater Systems: In industrial plants where pipes with high thermal stability are the only choices, RTR pipes can avoid deformation, handling such dilemmas with the least maintenance costs included. (Source: ResearchGate)
- Wastewater and Drainage: RTR pipes are one of the top choices in wastewater treatment due to their good resilience under pressure and chemical damage.
- Drinking Water Systems: In the cities where potable water must be everywhere, RTR pipes handle this fluid with no changes in the quality of water for the consumers over their long lifespan.
What Are the Beneficial Aspects of RTR Pipes?
The advantages of RTR pipes do not just come from their ability to take fluids over long distances without corrosion. They are more efficient than they seem. Check the aspect below for their magnificent strengths.
● Corrosion Resistance
The choice of resin makes them perfect in the case of corrosion on both internal and external sides in harsh and chemical environments like desalination or chemical processing.
● Smooth Internal Surface
The resin inner layer of RTR pipes allows them to be used as a reducer of pumping energy in every direction of pipelines.
● Lightweight
One magnificent point of RTR pipes is their high strength-to-weight ratio compared to old-fashioned metal pipes that were hard to handle in every location. This matter can decrease the cost of maintenance and transportation.
● Keeping The Pipes Away From Extra Protection
In the case of metal pipes that require periodic added cathodic protective layers, RTR pipes last for decades with no extra layer due to their design of resin and glass fibers.
● Long Lifespan
After all, the combination of these profits results in RTR pipes’ long lifecycle that can moderate the high initial cost compared to their alternatives by lasting longer than them.
Limitations and Risk Considerations of RTR Pipes
Unlike their flawless properties, RTR pipes may show some flaws during their lifetime, which every engineer must consider in their feasibility study before pipe selection.
First, they require UV protection layers due to their weakness to UV light, and they may degrade over time. The exposure to sunlight makes pipes fail in aboveground installations.
Second, the impact resistance of RTR pipes compared to steel pipes is another controversial issue among professionals in this industry. They may show more damage to physical objects during handling or transportation. Though this matter gets lighter with their easier handling process (lightweight comes to the ring!).
Third, however, the installation process of RTR pipes includes various methods that ease the process in multiple sites, from sensitive and seismic zones to irrigation lines above the ground, which require professional workers and tools for this process.
Fourth, the case of joints in RTR pipes that contain different methods is a crucial point, as neglecting it or making a mistake in the method selection can lead to leakages and ruin the whole system.
Last, consider that RTR pipe, besides the ability of all RTR pipes under corrosive conditions, the rate of harshness in each site must be aligned with the resin type used in their material composition.
Comparison with Other Pipe Materials
Let’s compare RTR pipes with their alternative in this section just to make sure there is no chance of being torn between two options.
1. RTR vs. Carbon Steel
RTR pipes come with a better level of corrosion resistance due to their resin layers compared to carbon steel pipes that require multiple protection layers.
2. RTR vs. HDPE
RTR pipes can be used instead of HDPE pipes where lightweight, besides the corrosion resistance and ability to take heavy loads, matter the most.
3. RTR vs. Lined Steel
RTR pipes can easily surpass steel pipes with their lighter weight and corrosion-free action under a corrosive environment. Also, they include more efficiency compared to steel pipes, which beat them in every aspect.
4. RTR vs. DI Pipes
About these two, just consider that unlike the DI pipe that corrodes easily and can last just about 25-40 years, RTR pipes in the same protection can last over half a century or more (about a hundred years under certain conditions).
5. RTR vs. uPVC
RTR pipes shine where UPVC pipes fail, especially in high-pressure systems, where UPVC pipes get deformed. Moreover, RTR pipes show a better performance under heat in firewater systems.
Now, check the table below for a better understanding of their properties. This table helps you to come up with a clearer cost/lifetime analysis.
| Material | Corrosion Resistance | Pressure Handling | Lifespan | Installation Cost | Maintenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RTR | Excellent | High | Long | Moderate | Low |
| Carbon Steel | Low | High | Medium | Low | High |
| HDPE | Good | Medium | Medium | Low | Low |
| Lined Steel | Moderate | High | Medium | High | Moderate |
| DI Pipes | Low | High | Medium | Moderate | High |
| uPVC | Good | Low | Medium | Low | Low |
That’s why the selection of the RTR pipes over their alternatives seems to be a more rational and reliable decision over time.
Final Wrap-Up
Finally, we’ve got to the last station. The case of RTR pipes is a magnificent and trusted choice for engineers and contractors when choosing a pipe material for their project. This pipeline satisfies all their requirements and can be designed in a way they request to be adapted to the project demands. At last, choose RTR pipes when a corrosion-free, high-pressure, temperature-resistant, and lightweight pipe is needed.
Frequently Asked Questions for RTR Pipes
1- What are RTR pipes?
RTR pipes are made of thermosetting resin such as polyester, vinyl ester, or epoxy; each can improve specific properties like resistance to chemicals or high temperatures in oil and gas or chemical plants.
2- What are the different types of RTR pipes?
The resin type used in each of GRP, GRV, or GRE pipes indicates how they’ll behave under heavy loads and harsh conditions.
3- What are the main advantages of RTR pipes?
RTR pipes are light, corrosion-free, and resistant to high-pressure flows with no deformation or degradation included.
about
The Author
Farshid Tavakoli is a seasoned professional in engineering and international trade. Holding degrees in Electrical Engineering, Mechatronics, and a Doctorate in Business Administration (DBA) from the University of Lyon, he also has a strong background in industrial automation and production line technologies.
For over 17 years, he has led an international trading company, gaining deep expertise in commercial solutions tailored to industrial needs. With more than 8 years of active involvement in infrastructure development, he specializes in the supply of electromechanical equipment for water and wastewater treatment plants and transfer projects.
Together with comapny expert team, he now provides consultancy and integrated solutions for sourcing and implementing complex infrastructure projects across the region.





