Do you think acid-resistant pipes are attacked only by harsh fluids? You’re probably wrong! Chemical processing, fertilizer production, and metal refining are just a few examples of acid corrosion cases, when pipes are usually facing microbiological corrosion caused by microorganisms. This matter requires a protective external layer, which raises the cost considerations.
The proper selection of acid-resistant pipe goes beyond materials; it’s about reliability, safety, and long-term cost of both material and maintenance. LineCore Pipes Group provides high-quality composite solutions like GRP, GRV, GRVE, and GRE pipes.
What Is an Acid-Resistant Pipe?
An acid-resistant pipe refers to a piping system that is made of materials that can resist corrosive and acidic conditions without degradation or damage.
These acidic substances can be acidic themselves or fluids that react and convert to acids.
Chemical Mechanism
The chemical reaction of acid and pipe material can be varied. For instance, metal oxidation results in rust and physical damage, while polymer degradation breaks the pipe’s function down and if chosen wrongly, causing cracks and leaks (ScienceDirect).
Check the table below for properties that create an acid-resistant pipe:
| Property | Description | Typical Values |
|---|---|---|
| pH Tolerance | Resists damage from acidic/alkaline solutions. | pH 0-14 (material dependent) |
| Diffusion Barrier | Prevents corrosive penetration. | 0.1-10 μm (material dependent) |
| Chemical Stability | Maintains integrity in aggressive chemicals. | Varies by chemical |
| Temperature Endurance | Resists high industrial temperatures. | Up to 120°C (material dependent) |
Where Are Acid-Resistant Pipes Used?
In highly corrosive sites and applications where acidic environments or fluids are available, an acid-resistant pipeline can ensure the durability and long-term performance. Here are the most-used piping cases that require acid-resistant pipe to survive.
1. Chemical Process Plants
Consider sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid, and how corrosive they are. Then, logically, an acid-resistant pipe that lasts acid production units is required to transport these harsh fluids with no leakage included.
2. Acidic Wastewater or Neutralization Systems
In mining, industrial plants, or some desalination systems where acidic wastewater has been found, it’s necessary to place acid-resistant pipes to transport that fluid to neutralization tanks without damage from extreme effluents. (Source: Amiblu)
Tip: These tanks themselves are made of composite materials to resist harsh fluids.
3. Mining and Metal Refining
In mining and metal refining, some chemical reactions produce a significant number of acids, and acids themselves are used to extract metals. Then, an acid-resistant material for pipelines will avoid further maintenance or repairs.
4. Fertilizer, Pulp & Paper, and Power Plants
In these industries, acid-resistant pipes are used to handle aggressive chemicals involved in production, waste treatment, and power generation processes.
5. Pharmaceutical and Food Processing Industries
Acid-resistant pipes are the hero for food processing lines where food hygiene is the most crucial consideration, and contractors usually use composite pipes for the transportation of chemicals, acids, and other harsh substances.
6. Acid Fume Extraction and Ventilation Systems
Acid-resistant pipes are used when fume extraction and ventilation require such pipes with high performance under high-temperature systems in production lines with no acid fumes.
Survey of All Pipe Materials Used for Acid Resistance
There are several materials used for acid-resistant piping systems. Each of these choices includes its own specific characteristics, helping the system last over decades with the least repair requirements.
Metal Piping Systems: Resistant Under Heavy Load, Fail in Harsh Environments
Metallic pipes are old-fashioned types of pipelines that can handle high-pressure systems, but are heavy and not resistant to aggressive fluids, and require extra protective liners and coatings.
Based on ScienceDirect, Stainless Steel Pipes, such as 304, 426, and 904L, can tolerate more moderate acidic conditions, but they include costly maintenance over time and should be inspected continuously.
Super Duplex and Nickel Alloys (Inconel, Hastelloy) are highly resistant to acids and alkalis. What makes them fail is heavyweight, expensive material, and weakness in localized corrosion.
Carbon Steel with Lining, which is more cost-effective than other metallic pipes, but should be replaced sooner than alternatives due to a lack of acid tolerance.
- Ending Note: Metallic pipes are highly resistant to external loads, but are notorious for their poor corrosion resistance and installation process due to their heaviness.
Plastic and Thermoplastic Systems
Plastic pipes are counted as modern solutions in the piping world. They are mainly lightweight and easy to handle. However, there are some arguments about their corrosion and pressure resistance. Let’s check them all:
- PVC: They shine in corrosive areas, but they fail in high temperatures and are highly sensitive to UV light (require expensive coatings).
- CPVC: More resistant than PVC in high-heat conditions, but still fails in high-pressure applications under the sun exposure.
- HDPE: These are the best option among thermoplastic pipes with the highest range of corrosion resistance. (Warning: fails under high pressures due to high flexibility)
- PVDF: Acts effectively under aggressive and acidic conditions but requires extra coating for UV exposure and probably fails under high-pressure loads.
- ECTFE: One of the best thermoplastic pipes for acid resistance, but it is vulnerable to UV light, and can not be placed under heavy traffic zones.
Finally, these pipes can be used for small- to medium-scale lines with low burial depth and no UV light included.
Rubber and Elastomeric Hoses
Elastomeric hoses are highly flexible and resistant to corrosive acids, but they are structurally weak and fail under high pressures with permanent installations.
- Pure Gum Rubber: Flexible, acid-resistant, not for permanent use. (Source: Scribd)
- Hypalon®: Flexible, acid-resistant, not durable long-term.
- Viton®: Flexible, chemical-resistant, not for permanent setups.
Try not to choose rubber pipes for permanent use cases and just install them for temporary uses.
Composite Systems (GRP, GRV, GRVE, GRE)
Composite pipes are one of the newest solutions in the pipe market, which are lightweight and resistant. The only thing that can make engineers concerned is the initial cost, which is offset by the lower overall cost compared to alternatives.
- GRP: Used for general uses and has a moderate rate of corrosion resistance against acidic conditions.
- GRV: With vinyl ester resin, it can resist the harshest acids with no degradation.
- GRVE: A combination of epoxy and vinyl ester resin that shines in acidic areas like chemical transmissions.
- GRE: Epoxy resin makes it resistant to heat more than acids, but may not show that tolerance under acidic conditions.
In the end, composite pipes are both cost-effective and highly resistant to acids. Then. Choose each type of them based on your project requirements.
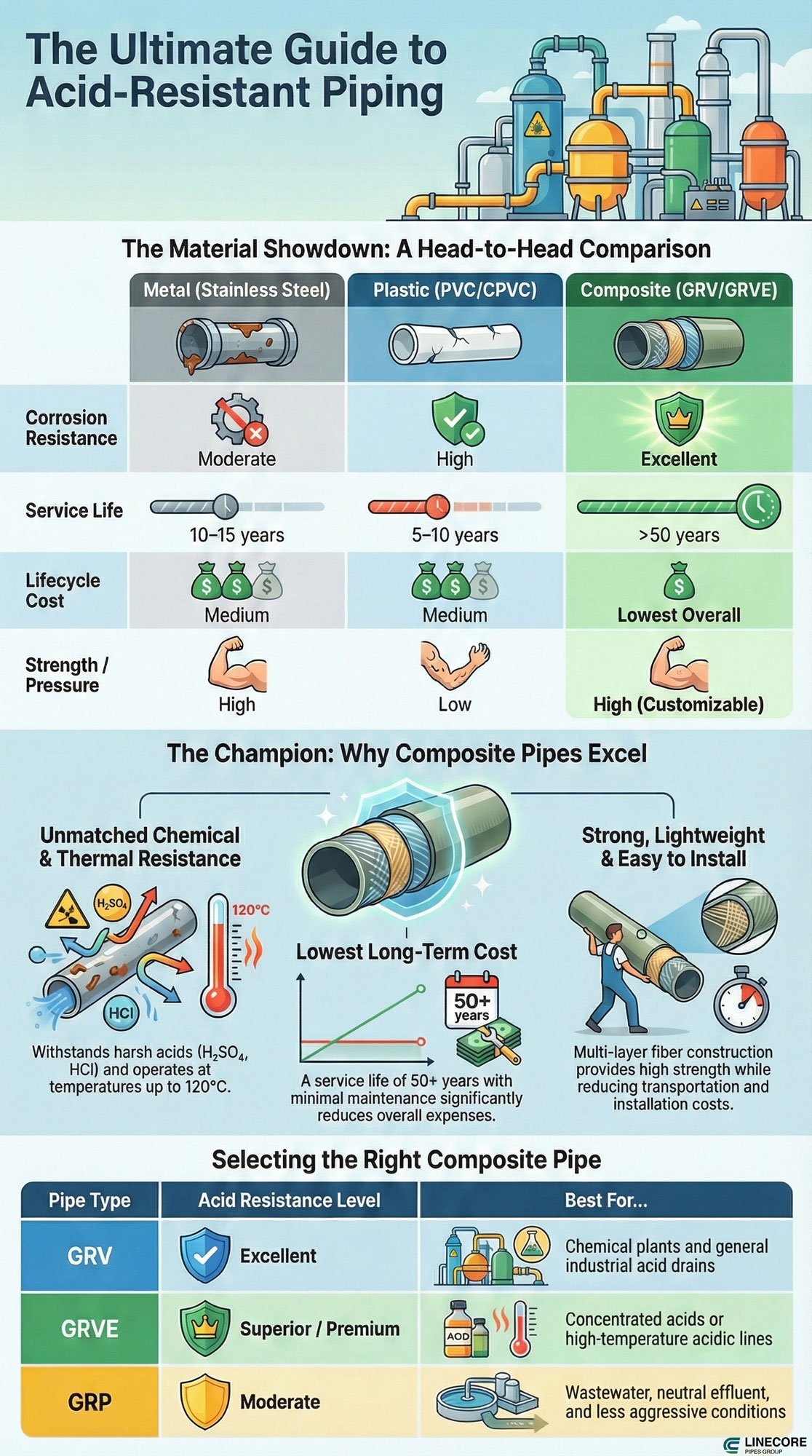
Overall Comparison of Acid-Resistant Pipes: Composite vs Metal vs Plastic
Once you have a comprehensive understanding of what acid-resistant pipes refer to and their material examples, it’s time to compare these materials to check which can better satisfy your project demands.
| Feature | Metal (SS316) | Plastic (PVC/CPVC) | Composite (GRV/GRVE) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | Heavy | Light | Light |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate | High | Excellent |
| Strength / Pressure | High | Low | High (customizable) |
| Temperature | Up to 150 °C | Up to 80 °C | Up to 120 °C |
| Maintenance | High | Medium | Very Low |
| Service Life | 10–15 years | 5–10 years | >50 years |
| Lifecycle Cost | Medium | Medium | Lowest overall |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate (specific acids) | High (broad range) | Excellent (wide range) |
| UV Resistance | Poor | Low (UV degradation) | High (UV-stable) |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate | Low | High (resistant to cracks) |
| Pressure Rating | High | Low (varies by type) | High (customizable) |
| Installation Cost | High | Low | Medium to High |
| Flexibility | Rigid | Flexible | Rigid (but customizable) |
| Environmental Impact | High (mining & processing) | Low (recyclable) | Low (can be recycled) |
The table above clearly shows the superiority of composite pipes in acidic use cases. Now let’s check which one of them is the best option for your project.
Composite Pipe Explained as Non-Metallic Chemical Piping: GRV, GRVE, GRP, and GRE Pipes
What makes composite pipes the best is their layering and the resin type used in several layers to handle both internal and external corrosion.
Structure: Three Base Layers of Composite Pipes
The structure of composite pipes is designed based on three main layers:
- Inner layer: This layer contains liners of resin that resist corrosion in acid handling, while their smooth inner surface comes from the centrifugal casting and reduces the need for pricy pumping energy.
- Structural Layer: The integrity of pipes roots in this layer. The choice of glass fiber and its density indicates how pipes perform under high-pressure flows and loads. Also, this layer is in charge of resistance to stress and physical problems.
- Outer Protection Layer: This layer is where composite pipes surpass metal ones. A resin-rich layer that protects pipes from several types of damage, such as corrosion, UV exposure, or physical issues like abrasion.
The Choice of Resin Type
FRP pipe family’s specification crucially depends on the resin type. There are three resin types, such as polyester, vinyl ester, and epoxy, that each improve specific aspects in pipes.
- Unsaturated Polyester (GRP): Glass-reinforced plastic pipes are an economical and general choice for moderate conditions of microbiological corrosion that are not as harsh as acid production lines.
- Vinyl Ester (GRV): This resin type resists under both organic and inorganic acids with a smooth inner surface that shows neither rust nor friction in chemical processing lines.
- Vinyl Ester-Epoxy Hybrid (GRVE): The highest rate of resistance among GRP family pipes. The combination of epoxy and vinyl ester makes them perfect for systems with high temperatures and a risk of aggressive acids.
- Epoxy (GRE): GRE pipes are famous for their high heat resistance in oil and gas pipelines, where hydrocarbon and alkaline transmission require such chemical-resistant pipelines.
Customization Options of Composite Pipes
Composite pipes can be designed in a way that suits the project requirements. Here are the specifications you can change in pipeline design to be aligned with your wants.
- pressure class
- stiffness
- wall thickness
- resin selection
- joint type
- installation method
- color
- diameter size
- length
GRP vs GRV vs GRVE vs GRE: Which One Is Best for Acidic Media?
Once you found GRP family the best option for your project, it’s time to choose a type to avoid any further waste of money or material. For instance, if you choose GRVE for a moderate environment, while a GRP pipeline works there more effectively.
Below, we bring you a comparison table of GRP, GRV, GRVE, and GRE pipes to help you make the best selection.
| Property | GRP | GRV | GRVE | GRE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resin Type | Polyester | Vinyl Ester | Vinyl Ester–Epoxy | Epoxy |
| Acid Resistance | Moderate | Excellent | Superior / Premium | Limited |
| Temperature Limit | 70–80 °C | 100–110 °C | 120 °C+ | 120 °C |
| Mechanical Strength | High | High | Very High | Very High |
| Cost Level | Low | Medium | Medium-High | Medium |
| Pressure Rating | Medium | High | High | High |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate | High | Very High | High |
| UV Resistance | Poor | Moderate | High | Moderate |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate | Excellent | Superior | Limited |
| Lifespan | 10-15 years | 15-25 years | 25-50 years | 10-20 years |
| Best Use Case | Wastewater, neutral effluent | Chemical plants, acid drains | Concentrated acid or high-temp acid lines | Alkalis, hydrocarbons |
In summary:
GRV: Best overall acid-resistant solution for industrial applications by being both cost-effective and highly resistant to acids and chemicals.
GRVE: A pro-choice for acid production lines and extremely aggressive chemicals, where high temperature requires double strength.
GRP: Choose GRP pipes for more moderate cases, like organic acid liners or applications with a low risk of acidic reaction.
GRE: Not really recommended for acidic areas, better used in hydrocarbons and alkali transmission lines.
Why Composite (GRV/GRVE) Pipes Outperform Other Materials
Composite pipes are such resistant pipelines in acid production systems with low requirements for maintenance or repair, making them the best option among alternatives. But it’s not the only reason why you should choose composite pipes over other materials. That’s why:
Chemical & Thermal Resistance
The vinyl ester matrix allows GRV and GRVE pipes to be used for a range of corrosive acids that include sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄), hydrochloric acid (HCl), nitric acid (HNO₃), and hydrofluoric acid (HF). (ResearchGate) These pipes must remain the same in high temperatures.
- Resists H₂SO₄, HCl, HNO₃, HF, and oxidizing acids
- Stable operation up to 120 °C
Structural Strength
Composite pipes are designed in multiple layers and directions with glass fibers that make them both lightweight and easy to handle. They can also resist stress, vibration, heavy traffic, and external loads without deformation.
- High tensile, hoop, and axial strength
- Excellent impact, vibration, and fatigue resistance
Lifecycle Cost & Sustainability
FRP piping systems are designed to last over 50 years with the least requirement of pricy maintenance in deep burials and underground installations. GRV and GRVE pipes show no corrosion, and their lightweight reduces the cost of installation and heavy cranes for transportation.
- Can be manufactured in long lengths
- No internal coating or cathodic protection
- Lightweight for reduced installation cost and carbon footprint
Maintenance Advantages
GRV and GRVE pipes are corrosion-free, which require minimal maintenance and inspection over time in hard-to-access sites. Also, they include a lower downtime in sensitive conditions as a cost-effective solution for piping systems.
Applications of GRV/GRVE Composite Acid-Resistant Pipes
Due to the good resistance of acid-resistant composite pipes, engineers and contractors choose them for their acid-containing projects. Here are the most-used cases of GRV, GRVE, GRP, and GRE pipes:
- Acid Production Lines: These pipes are great for transportation and storage of acids like sulfuric acid, which makes them safe to use in production settings.
- Chemical Waste and Neutralization Lines: These lines are used in systems that are meant to handle and neutralize harmful chemical waste. They are highly resistant to corrosion against harsh acids.
- Fertilizer and Mining Acid Pipelines: GRV and GRVE pipes are the best option for acid transmission lines where inorganic acids threaten the pipes for corrosion or abrasion.
- Power Plant Flue Gas Desulfurization Systems: These systems include such an amount of sulfur dioxide that results in acidic material surrounding the pipelines, where only GRV and GRVE pipes can tolerate the situation.
- Acidic Drainage and Scrubber Systems: The acidic wastewater of scrubber systems presents another issue in piping systems, which require more thoughtful planning and pipe selection, such as GRV or GRVE pipes.
- Exhaust and Fume Extraction Ducts: Used in systems to eliminate acidic fumes released from industrial processes for long-term efficiency without degradation.
Your Partner in Composite Corrosion Solutions: LineCore Pipes Group
LineCore Pipes Group specializes in composite corrosion solutions, including customized pipelines with specific resin selection and fabrication for acid-resistant applications. We provide our customers a wide range of GRV, GRVE, GRP, and GRE pipes, their fittings, and jointing pieces that are aligned with site conditions and resin formulations.
Our services include EPC solutions, technical support, and lifecycle services. Contact info@PipeLinceCoreGroup.com for expertise on your project today!
FAQs
1- What is the best pipeline option for acidic conditions?
GRV and GRVE pipes from the composite pipes’ family are the best suited for harsh and acidic chemical processing with lightweight and durability.
2- How long do GRV and GRVE pipes last?
GRV and GRVE pipes can last over 50 years and more under certain conditions and reliable backfilling under deep burials.
3- What makes composite pipes better than metal or plastic pipes in acidic conditions?
Composite pipes are lightweight, corrosion-free, pressure- and temperature-resistant pipes that include a longer lifespan with fewer requirements for maintenance or constant inspections.
about
The Author
Farshid Tavakoli is a seasoned professional in engineering and international trade. Holding degrees in Electrical Engineering, Mechatronics, and a Doctorate in Business Administration (DBA) from the University of Lyon, he also has a strong background in industrial automation and production line technologies.
For over 17 years, he has led an international trading company, gaining deep expertise in commercial solutions tailored to industrial needs. With more than 8 years of active involvement in infrastructure development, he specializes in the supply of electromechanical equipment for water and wastewater treatment plants and transfer projects.
Together with comapny expert team, he now provides consultancy and integrated solutions for sourcing and implementing complex infrastructure projects across the region.