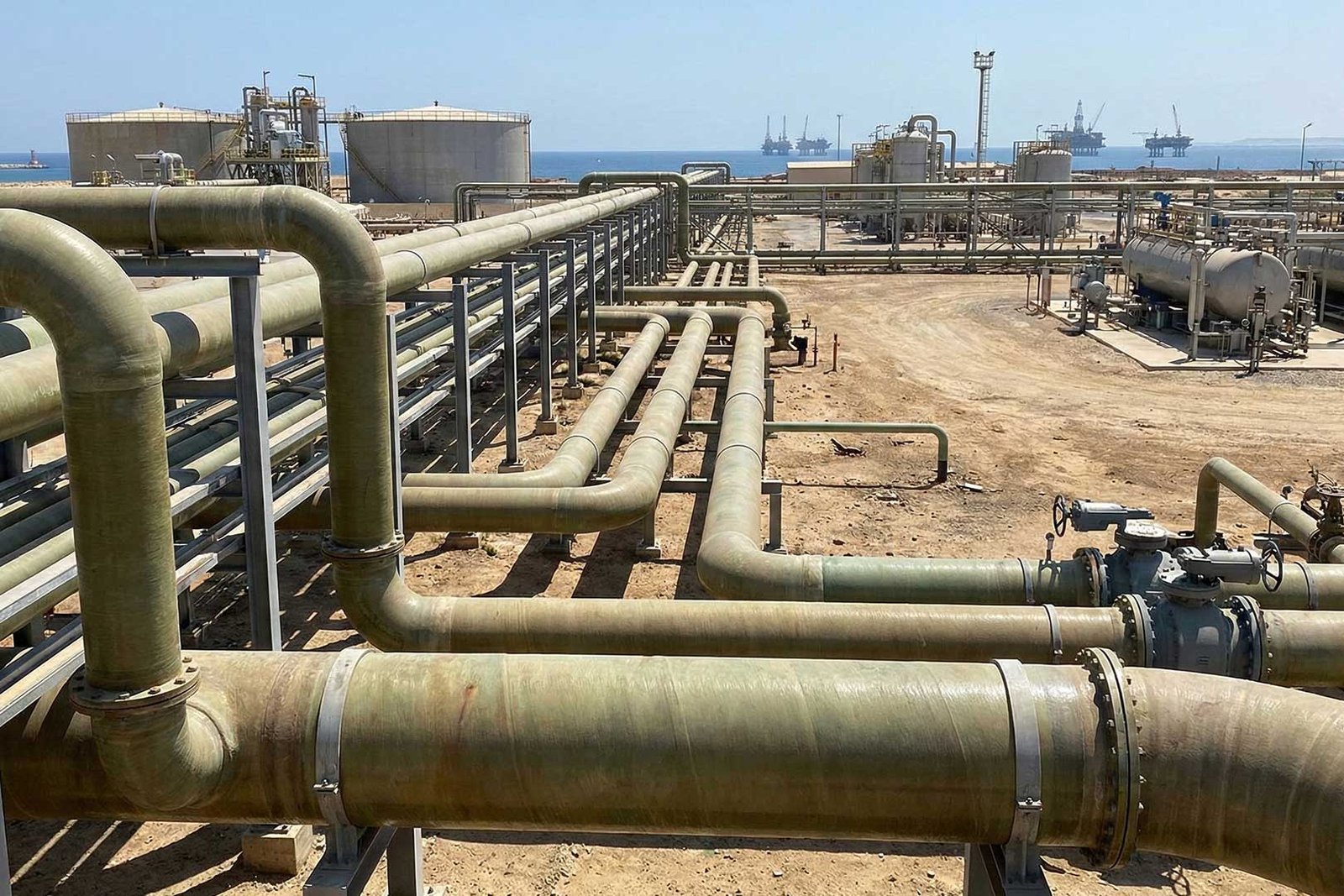
What pipe can resist under scorching UV light or aggressive saline conditions? GRE pipes are not only used popularly as modern solutions for oil and gas plants, but also work in various industrial use cases. The multilayer design of GRP pipes provides a long lifespan with minimal maintenance for over 50 years.
This post represents six main categories of where GRE pipes are used, from offshore to aggressive soils in irrigation lines. Stay tuned till the end for all these sections.
How To Design GRE Pipes for Specific Applications?
GRE pipes can be designed based on the project requirements. As the balance of glass fiber and epoxy resin may be modified, or additives may make some changes in thermal stability or strength in harsh conditions.
Materials Used in GRE Pipes
As noted in Future Pipe, GRE pipes are made of E-glass fibers soaked in epoxy resin or sprayed with resin. Fibers add strength to the pipes that help handle both internal and external pressure, while the resin layer can avoid chemical reactions such as corrosion or thermal issues.
The Manufacturing Method: The Case Filament Winding
The process of winding glass fibers around a mandrel to shape pipes is called filament winding. Soaked fibers in epoxy can resist both axial and hoop forces, while surviving over 1 million pressure cycles at 120 °C (ASTM D2992).
How To Customize Mechanical Features?
GRE pipes can be manufactured in a way that tolerates various conditions and pressures. Check points below to match the pipes with your project demand:
- Wall Thickness: 5–50 mm for any pressure rating
- Winding Angles: 90° = max burst strength, 45° = better flexibility
- Fire-Retardant: Resists 900 °C for 30 min (ASTM E84)
- UV Protection: <5 % strength loss after 5 years outdoors
- Conductive: <10⁹ Ω/m for ATEX/explosive zones
| Feature | Customize By | Range / Value | Benefit | Use Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wall Thickness | More layers | 5–50 mm | Higher pressure | Injection / desalination |
| Winding Angle | Helix angle | 45°–90° | Strength or flexibility | Offshore bends / long runs |
| Fire-Retardant | Phenolic resin | 900 °C / 30 min | Fire survival | Firewater / platforms |
| UV Protection | Outer veil + blockers | <5 % loss (5 yrs) | Outdoor life | Desert / topside |
| Conductive | Carbon filler | <10⁹ Ω/m | Spark-safe | Explosive zones / fuel |
| Abrasion Liner | Thick inner layer | +1–3 mm | Sand-proof | Produced water |
| High-Temp Resin | Novolac epoxy | 120–150 °C | Hot service | Geothermal / CCUS |
Now let’s dive into the main classifications of the GRE pipe applications: oil & gas, marine and shipbuilding, industrial systems, and water infrastructures.
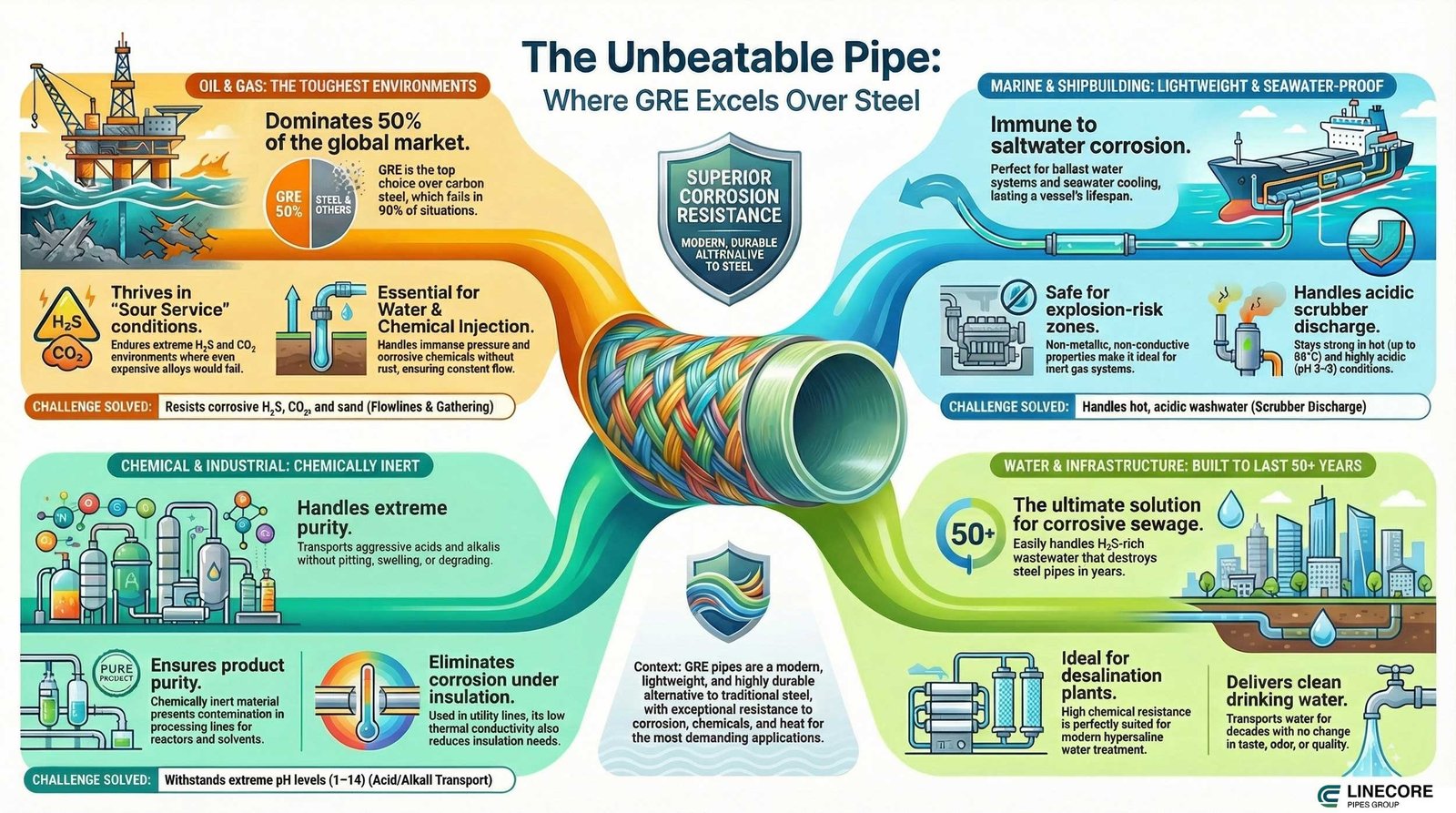
GRE pipe uses infographic (source: pipelinecoregroup.com)
The Biggest Share: GRE Pipes in Oil & Gas
Oil and gas are valued for about half the global GRE market, which is reaching more quickly. Unlike carbon steel, which fails in 90% of situations, GRE pipes are the top choice for engineers.
- Water Injection Seawater or produced water, under immense pressure, is injected far below the surface. GRE’s resistance to rust means it can keep things moving without a hitch for years.
- Chemical Injection Tiny lines carry methanol, inhibitors, and biocides directly to the wellhead. The epoxy used is tough enough to withstand acids and other harsh conditions.
- Flowlines & Gathering Crude oil, gas, sand, H₂S, CO₂? GRE handles it all. Inside, it remains smooth, unaffected by harsh environments.
- Hot, salty, and gassy environments? GRE takes it all, and it’s still light enough for quick offshore installations.
- Firewater Systems When fire threatens a platform, GRE’s fire-retardant properties make it stay intact, allowing water to keep flowing. Offshore Utilities
- Cooling lines, service water, inert gas, and drains, GRE shows a lighter alternative, eliminating the need for painting and the problems of corrosion.
- Sour Service (High H₂S/CO₂) In places where carbon steel fails and expensive alloys are the norm, GRE quietly endures, lasting for decades. (Source: ResearchGate)
In the most demanding areas of the oil and gas industry, GRE pipes have proven to be the intelligent, hassle-free alternative to steel.
GRE Pipe Applications in Marine & Shipbuilding
Due to the good resistance of GRE pipes in saltwater and marine conditions, engineers choose them over steel where low downtime requires lighter pipes.
- Ballast Water Systems: Best for saltwater and chlorine transmission with no cracks or leaks in the vessel’s lifespan.
- Scrubber Discharge Lines: In acidic and hot conditions, GRE can stay strong in pH 3–5 and 80 °C, while keeping the installation easy in engine rooms.
- IG Systems: The inert gas systems use GRE pipes for a non-conductive and spark-free connection in nitrogen transmission of cargo tanks.
- Seawater Cooling: With a smooth inner surface, GRE pipes run saltwater constantly with no need for replacement.
- Explosion-risk zones require non-metallic pipes such as composite pipes. GRE pipes can lead the way of AXEX rules with no corrosion or leak included. (Source: ScienceDirect)
GRE Pipe Uses in Chemical & Industrial Plants
Chemical plants are tough on pipes. Acids, alkalis, heat, and constant washdowns take their toll. But GRE keeps running, while steel, and even stainless steel, succumb to corrosion.
1. Acid & Alkali Transport Lines
Sulfuric, hydrochloric, caustic soda – GRE handles pH levels from 1 to 14 without pitting or swelling.
2. Chemical Processing Lines
There’s no need for specialized alloys. Chemical Processing Pipelines From reactor feeds to solvent recovery, GRE remains chemically inert. This ensures product purity and prevents leaks.
3. Utility Lines
Cooling loops, brine circulation, and service water systems benefit from GRE’s low thermal conductivity, which reduces insulation needs and eliminates corrosion under lagging.
4. Corrosive Drainage
Floor drains, neutralization pits, and spill containment systems rely on GRE to handle the most aggressive mixtures, directing them straight to treatment without deterioration.
GRE Pipe Uses in Water & Infrastructure Projects
Water infrastructures face corrosion more than other applications, and GRE pipes can transport water in urban areas or be used in desalination plants.
- Drinking Water: To transport water across deserts and cities to last for decades with no taste or odor change.
- Water Networks: Both raw and industrial water lines require pipes that can withstand UV light, pressure, and sediments in pump stations and factory supplies.
- Wastewater & Sewage Pipelines: H₂S-rich sewage eats steel alive. GRE shrugs it off and keeps flowing, even underground for 50+ years.
- Desalination Plants: GRE pipes with high chemical resistance can be used in modern desalination, mostly in the GCC area.
- Firewater Distributions: In underground installations and hot use cases, GRE pipe with additives can tolerate high temperatures for a limited time and under certain conditions.
- Chilled Water Systems: In cities where old infrastructures need to be replaced, GRE pipes are reliable choices that last for decades and transport water with no change in temperature or quality.
Now, check this table below for a quick understanding of GRE pipe uses across various industries in terms of pressure, temperature, and the reason they’re used there.
| # | Sector | Specific Use | Temp (°C) | Pressure | What Challenge Solved |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Oil & Gas | Water injection | 100–130 | Very high | Seawater corrosion |
| 2 | Chemical injection | Ambient | High | Acids & solvents | |
| 3 | Flowlines & gathering | 80–120 | High | H₂S + CO₂ + sand | |
| 4 | Produced water/hydrocarbons | 90–110 | Medium-high | Salty gassy soup | |
| 5 | Firewater systems | Ambient | Medium | Fire & heat | |
| 6 | Offshore utilities | 40–80 | Low-medium | Saltwater | |
| 7 | Sour service H₂S/CO₂ | 80–120 | High | Extreme corrosion | |
| 8 | Marine/Shipbuilding | Ballast water | Ambient | Low | Chlorinated seawater |
| 9 | Scrubber discharge | 60–80 | Low | Acidic washwater | |
| 10 | Inert gas systems | Ambient | Low | Explosion risk | |
| 11 | Seawater cooling & brine | 30–50 | Low-medium | Biofouling + salt | |
| 12 | Explosion-risk zones | Ambient | Low | Static sparks | |
| 13 | Chemical Plants | Acid/alkali transport | 60–100 | Medium | pH 1–14 |
| 14 | Process pipelines | 80–120 | Medium | Solvents & reagents | |
| 15 | Cooling water & brine | 40–90 | Low | Corrosion under insulation | |
| 16 | Corrosive drains & effluent | Ambient | Gravity | Spills & acids | |
| 17 | Water & Infrastructure | Potable water transmission | Ambient | Medium | Chlorine & taste |
| 18 | Raw/industrial water | Ambient | Medium | Sediment & chlorine | |
| 19 | Wastewater & sewage | Ambient | Low | H₂S gas | |
| 20 | Desalination intake/outfall | 30–40 | High | Hypersaline | |
| 21 | District cooling chilled water | 4–14 | Medium | Condensation | |
| 22 | Fire protection mains | Ambient | Medium | Fire emergency |
22 Real-World Applications: One pipe that resists every hardship with no rust or leak!
New Trends of GRE Uses in the Energy Transition
As the demand for new technologies in piping systems is rising so fast, GRE pipes are revolutionized by additives and fillers that improve where they failed before.
Geothermal Brine & High-Temp Lines
In the past, steel pipes failed under 150 °C+ silica-loaded brines. GRE pipes with high-Tg grades are the best option for such situations that work with no maintenance requirement in geometrical environments.
Offshore Wind Farm Utilities
Cooling, hydraulics, and service water on fixed and floating turbines. GRE drops weight, fights saltwater forever, and speeds installation.
Produced Water Reinjection
Where steel can’t resist, like hot and full of CO2 lines, GRE can take the high temperature, pressure, and the harsh chemicals with the least maintenance costs.
Why Engineers Use GRE Pipe Over Traditional Pipelines
GRE pipes with their lightweight, pressure, and corrosion resistance under heavy loads and corrosive environments. Engineers choose GRE pipes with confidence in real-world cases.
Reduced Life-Cycle Expenses
While GRE might seem pricier at the outset, its long-term performance is where it shines, easily outpacing steel and GRP over 25-30 years of lifespan.
- Think about it: no need for coatings, cathodic protection, corrosion fixes, or those costly emergency excavations. The end results? Total savings frequently exceed 50%. (Check Scribd)
Smooth Inner Surface Brings the Speedy Flow In
The interior remains perpetually glass-smooth. This translates to lower friction, which in turn means smaller pumps, reduced energy consumption, and often, smaller pipe diameters compared to steel, which tends to roughen quickly.
Light & Fast Install
It’s a quarter the weight of steel, and there’s no welding involved. The bonded joints cure in mere minutes. This means crews can work more quickly, cranes can be smaller, and offshore lay rates can double or even triple.
Almost Zero Maintenance
Once it’s installed, either buried or bolted onto the platform, you can practically forget about it. No painting, no inhibitor runs, and no rust issues to worry about – just a quick inspection every few years.
- Fire & Spark Safe: The fire-retardant grades can withstand intense fires. The fully non-conductive design eliminates stray currents and removes the risk of static electricity in explosive environments.
What Are the Limitations of GRE Pipes?
Every pipe may fail in some horrible cases. GRE pipes are sensitive to point loads because they are not very flexible and require sturdy bending. Then, the installation needs professional workers, and the initial costs may be higher than those of steel pipes.
Below, we bring you a table that points out the most-repeated limitations of the GRE pipes.
| Limitation | Issue | Quick Fix | Still Viable? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Impact sensitivity | Cracks from drops or rocks | Protective sleeves, rock-shield, careful handling | Yes |
| Low flexibility | Can’t do very tight bends | Respect min. bend radius, use more fittings | Yes |
| Needs skilled installers | Bad joints = leaks | Certified crews + proper adhesives | Yes |
| Higher upfront cost | Bigger initial budget hit | Focus on 20-30 years life-cycle savings | Yes |
Core Properties That Make GRE Pipes Unbeatable
There are several characteristics of GRE pipes that allow them to be fit in various use cases, from oil and gas pipelines to water supplies. Then check these four main properties that make such a change in their function:
- High Pressure & Hoop Strength: With a hoop strength of 300-450 MPa and working pressure tolerance up to 350 bar, GRE pipes can take both internal and external loads with no deformation.
- Temperature Resistance: The typical service range goes around 110 °C, which, with additives, can change to thousands in certain conditions. (What Is Piping)
- Chemical & Corrosion Resistance: In both high and low pH ratings, GRE pipes show no corrosion or degradation, unlike steel pipes, which may fail under acidic conditions.
- Low Thermal Conductivity: This material works when facing high temperatures and has a low electrical resistivity of>1012 Ω·cm with no static risk in dangerous sectors.
Conclusion: When to Choose the GRE
In summary, choose GRE over steel when the temperature goes above hundreds and pressure rates are higher than 300 bar. In fluid transportations like acids, alkalis, brine, or saltwater, GRE pipes show no corrosion or degradation and perfectly act for decades. In short, where steel may be killed by harsh conditions, GRE pipes stay strong with no changes as the long-lasting choice.
FAQs
1- What is the difference between GRE, GRV, and GRP pipes?
GRE pipes use a resin matrix compared to GRP (unsaturated polyester for general uses) and GRV (vinyl ester for chemical resistance). The epoxy allows pipes to resist higher pressure and temperatures than GRP and GRV pipes.
2- Can GRE pipes be used for potable water?
Yes, most manufacturers recommend NSF-61 and WRAS-certified GRE grades with no leaches included.
3- What is the maximum temperature for GRE pipes?
Standard epoxy: 110 °C in typical use cases, and novolac or special anhydride-cured grades can handle 130–150 °C continuous service.
4- Are GRE pipes fire-resistant?
Yes, Fire-retardant versions with additives verified by ASTM E84 Class 1, resist 900 °C for 30 min, and are used for firewater systems.
about
The Author
Farshid Tavakoli is a seasoned professional in engineering and international trade. Holding degrees in Electrical Engineering, Mechatronics, and a Doctorate in Business Administration (DBA) from the University of Lyon, he also has a strong background in industrial automation and production line technologies.
For over 17 years, he has led an international trading company, gaining deep expertise in commercial solutions tailored to industrial needs. With more than 8 years of active involvement in infrastructure development, he specializes in the supply of electromechanical equipment for water and wastewater treatment plants and transfer projects.
Together with comapny expert team, he now provides consultancy and integrated solutions for sourcing and implementing complex infrastructure projects across the region.





