More and more countries around the world are getting fresh water from the sea. Desalination is one of the fastest-growing businesses in the water sector in 2025. FurtuneBusinessInsights notes that to avoid water shortages, huge new plants are built in places like Saudi Arabia, the UAE, Morocco, and even Texas.
Desalination is more than just high-tech membranes and clean energy, though. There are hidden pipelines that bring seawater in and out under every plant. The right material for these lines can make or break a project’s long-term success. That’s where GRP pipes come to the ring as glass reinforced plastic pipes.
The Future of Desalination: How GRP Pipes Shaped These Plants
This year, the world’s desalination capacity has gone over 100 million cubic meters per day. The Middle East is in the lead, making about 60% of that. Saudi Arabia is spending more than 80 billion dollars on its own to double its capacity by 2030 (Source: SWCC).
- Real-World Example: The Taweelah plant in the UAE is the biggest reverse-osmosis plant in the world. It already gives out almost a billion liters of water every day.
Global Approaches to Desalination: What Other Countries Are Doing
Countries such as Morocco, China, and the United States are also getting involved, even though they are not in the Gulf.
- Case in Point: The Rabat project in Morocco, the northern coast plants in China, and the Galveston Bay plan in Texas all show how quickly desalination is spreading.
This global boom means that more pipes are being laid under the sea, which means they are exposed to salt more often. It also means that there is more demand for materials that won’t rust for decades.
What Are the Common Problems of Traditional Pipelines?
Metal pipelines don’t do well in seawater. Even when they are covered or protected with cathodic protection systems, steel and ductile iron still rust. The cost of constant maintenance adds up because coatings peel, welds crack, and so on. It costs a lot of money to replace these lines, and it often causes problems.
What’s The Solution? GRP Pipes: A Reliable Alternative for Corroded Pipes
Desalination plants use these pipelines to do their work. The whole operation can stop if an intake line breaks. That’s why engineers are moving away from metals and toward materials like GRP that are made to last in seawater.
What Makes GRP Pipe the Best Option for Desalination Plants?
Glass fibers and resin make up GRP, which is a strong, light composite. It doesn’t need paint or special linings, and it doesn’t rust or scale. International standards like AWWA C950 and ISO 10639 already cover it, so it is approved and trusted for big water projects.
- Summary: To put it simply, GRP pipes last longer, are lighter, and don’t need much care.
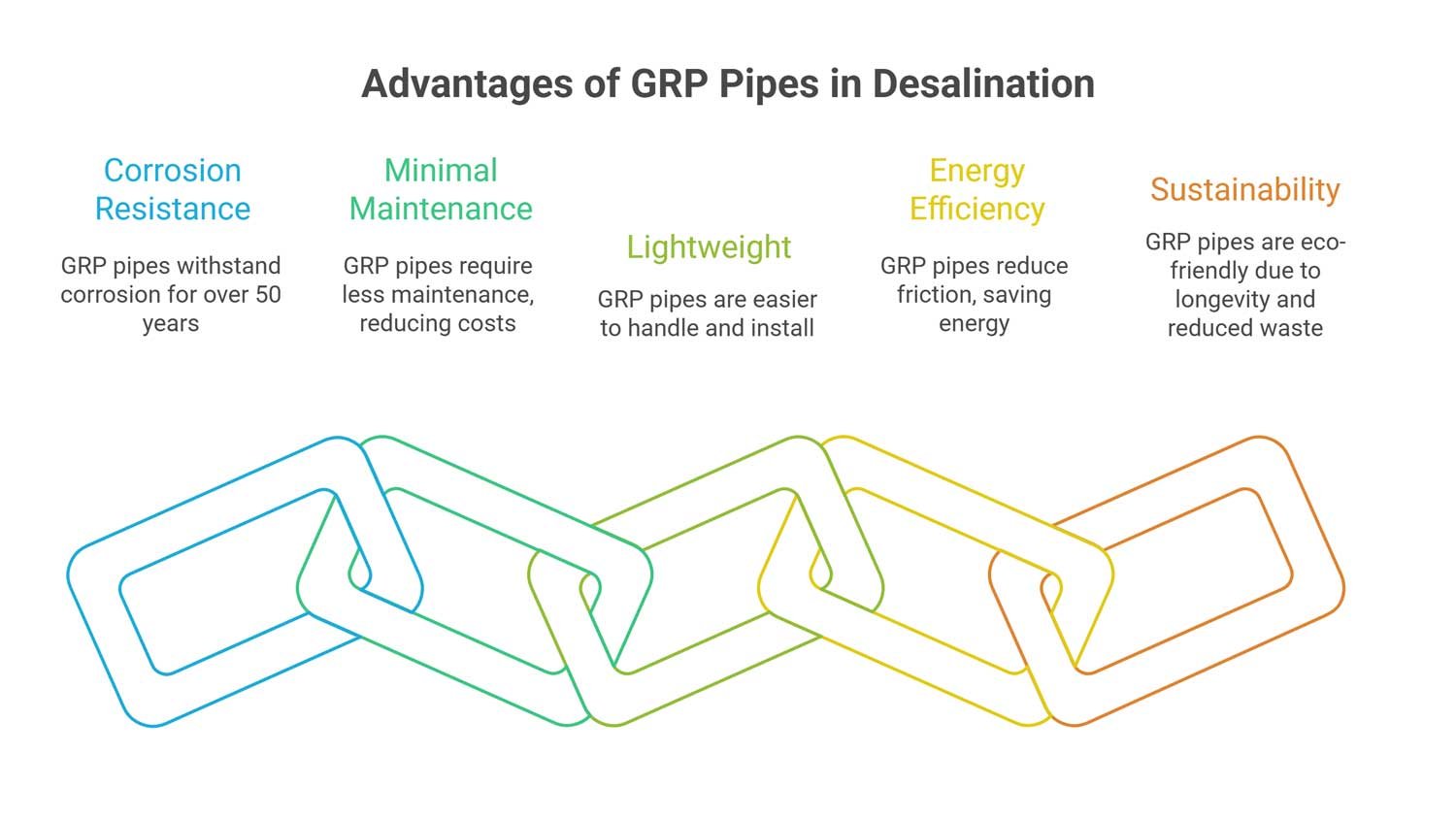
The Real Benefits of GRP
Let’s see how GRP pipe surpasses its alternative by its perfect characteristics in desalination plants. Whether due to its corrosion resistance or lightweight, GRP is the top choice for such aggressive projects.
1. Corrosion Resistance Over Decades
Salt and chemicals don’t hurt GRP naturally. Steel pipes in seawater often break down in 20 to 30 years. Some GRP pipelines have been around for more than 50 years, and some have been around for even longer. That means fewer things need to be replaced and costs will go down over time.
2. Minimal Maintenance, While Keeping Reliability on Top
No need to paint again, line again, or add electrical protection systems. The smooth inside stays clean, so the pumps don’t have to work as hard as the years go by. Many desalination plants that switched to GRP say their maintenance costs are now up to 60% lower.
3. Lightweight: Ease of Storage, Transportation, and Installation Process
Steel is about four times heavier than GRP. Smaller cranes can move it, and the joints fit together with flanges or push-fit, so welding isn’t needed. This makes it safer, faster, and less expensive to install.
4. Resin Nature and Energy Efficiency: Smooth Inner Surface
The smooth surface of GRP lowers the amount of friction that happens in the pipe. Pumps need less power to move the same amount of water because the Hazen-Williams coefficient is about 150 (compared to steel’s 120–130). That means real energy savings over the years.
5. Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Choice
There’s no metal pollution or coating waste because GRP lasts longer and doesn’t corrode. Fewer replacements mean less digging, less waste, and less CO₂ for environment and desalination plants.
Case Studies from the Field
This isn’t just a theory; GRP has already shown that it works. There are several real-world use cases that are mentioned below.
Sandefjord – Norway
As noted in the Source Magazine IWA, in Norway a piping system in seawater is inspected by engineers and surprisingly there were no corroded areas and pipes were in great mechanical condition. That’s why GRP pipes can be reliable choices for cold and saline environments.
Shanghai
A pipeline in length of 3.6 kilometers is installed via microtunneling and engineers have found no change in their smooth internal surface after many years of installation. The project has shown that GRP pipe effectively could manage the overall costs by minimizing the maintenance costs and pumping energy requirements. (Source: Amiblu)
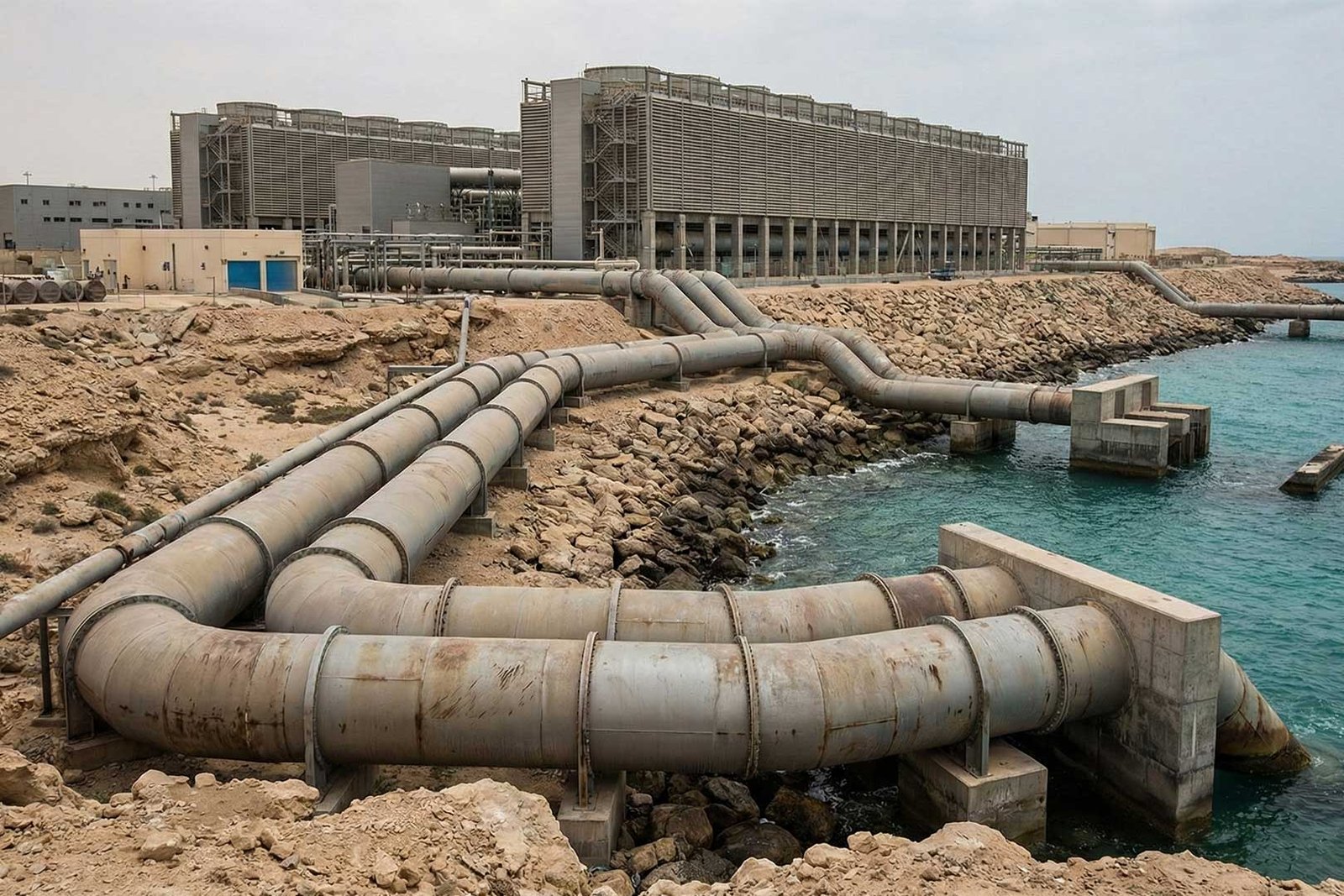
The Case of Gulf: Saudi Arabia and the UAE
Let’s come closer to the Gulf and check out the core desalination plants such as Ras Al-Khair in Saudi Arabia and Taweelah in the UAE that use GRP and GRE pipes for seawater intakes and discharge systems due to corrosion resistance, low downtime, easier maintenance compared to traditional alternatives like steel.
What Standards Support These Pipelines?
GRP pipe isn’t just used due to its well-performed characteristics, but it also follows international standards and guidelines to set the design, installation, and further operations at the same method in each project.
These standards below are some good examples of how GRP pipes can be supported by global rules and demands.
| Standard | What It Covers | Common Application |
|---|---|---|
| AWWA C950 | Fiberglass pressure pipes | Seawater intake and pressurized transmission systems |
| ISO 10639 | GRP piping for water and seawater | RO feed lines and raw seawater transport |
| ISO 10467 | GRP piping for drainage and outfalls | Brine discharge and gravity outfall systems |
| ISO 14692 | GRP systems for oil, gas, and marine environments | Offshore pipelines and marine cooling water |
| ASTM D3517 | Filament-wound GRP pipe design and testing | Manufacturing, qualification, and design validation |
Latest Trends of GRP Pipe’s Industry
GRP is no longer just a niche product; it’s becoming standard in seawater systems. The global market for GRP pipes is worth about $5 billion in 2024 and is growing steadily as more projects use them.
Many desalination and cooling projects have used GRP pipelines made by companies like Future Pipe Industries, Amiblu, and Amiantit. Utilities like how reliable it is over time, and contractors like how light and quick it is to install.
One engineer said, “The best pipeline is the one you never have to replace.”
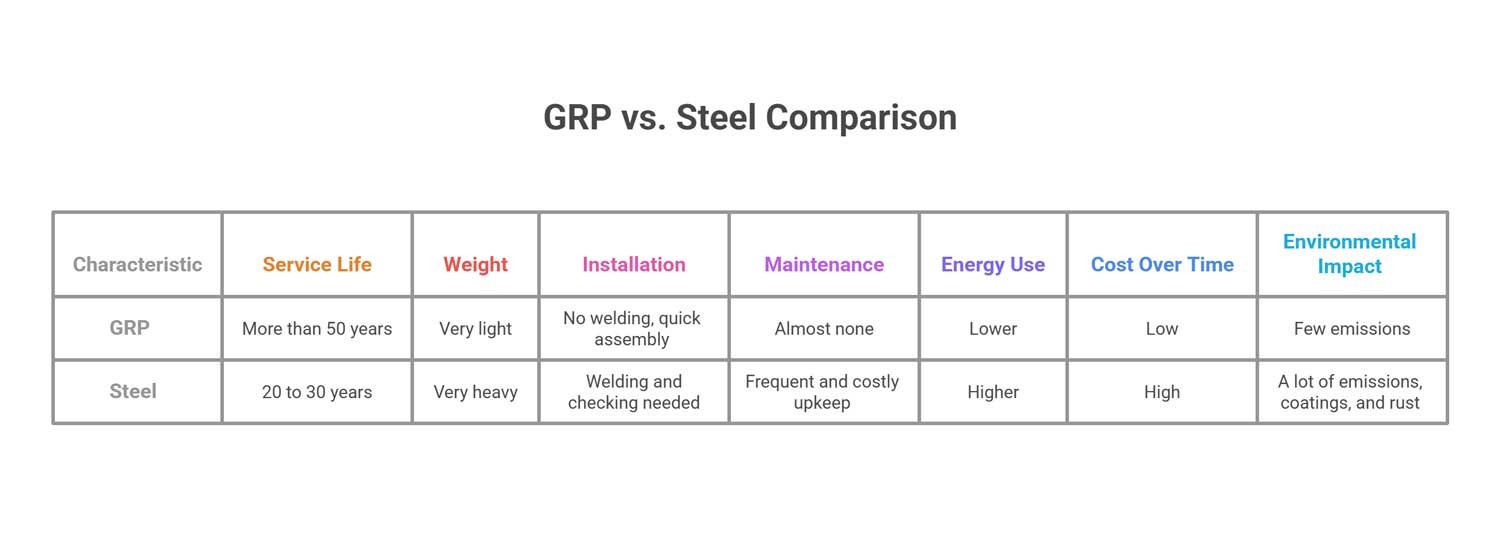
A Quick Look at GRP vs. Steel
The differences between GRP and steel are easy to see. As GRP doesn’t corrode or needs protective coatings and linings, steel pipes mostly require continuous maintenance, while the risk of cracks in steel pipe is so high.
- Life of Service: More than 50 years 20 to 30 years.
- Weight: Very light to very heavy.
- Installation: No welding, quick assembly Welding and checking are needed.
- Maintenance: Almost none for GRP, while steel requires frequent and costly upkeep.
- Energy Use: Lower with GRP because of its smoother inner wall; higher with steel due to its rough surface.
- Cost Over Time: Low to High Environmental impact Few emissions of GRP compared to a lot of emissions, coatings, and rust in steel pipe.
Looking Ahead
Desalination is here to stay. This is how a lot of countries are preparing themselves for enough water in the future. But for it to be truly sustainable, every part of the system, even the pipes, has to last.
Where GRP pipe comes to the scene
That long-term dependability is what GRP gives you. It doesn’t rust, it doesn’t pollute, and it makes installation safer and easier. It’s one of those reliable changes that makes sure that whole plants run smoothly behind the scenes.
GRP is going to be a big part of more desalination projects that start up between now and 2025 and beyond. The world needs materials that are smarter and stronger, and GRP is showing that it can be one of those.
Wrap-Up
In summary, GRP pipes ease the desalination plants pipeline selection through their special properties. We’ve discovered how fast and effectively each country uses GRP pipes in saline conditions for decades with no rust and corrosion included.
about
The Author
Farshid Tavakoli is a seasoned professional in engineering and international trade. Holding degrees in Electrical Engineering, Mechatronics, and a Doctorate in Business Administration (DBA) from the University of Lyon, he also has a strong background in industrial automation and production line technologies.
For over 17 years, he has led an international trading company, gaining deep expertise in commercial solutions tailored to industrial needs. With more than 8 years of active involvement in infrastructure development, he specializes in the supply of electromechanical equipment for water and wastewater treatment plants and transfer projects.
Together with comapny expert team, he now provides consultancy and integrated solutions for sourcing and implementing complex infrastructure projects across the region.