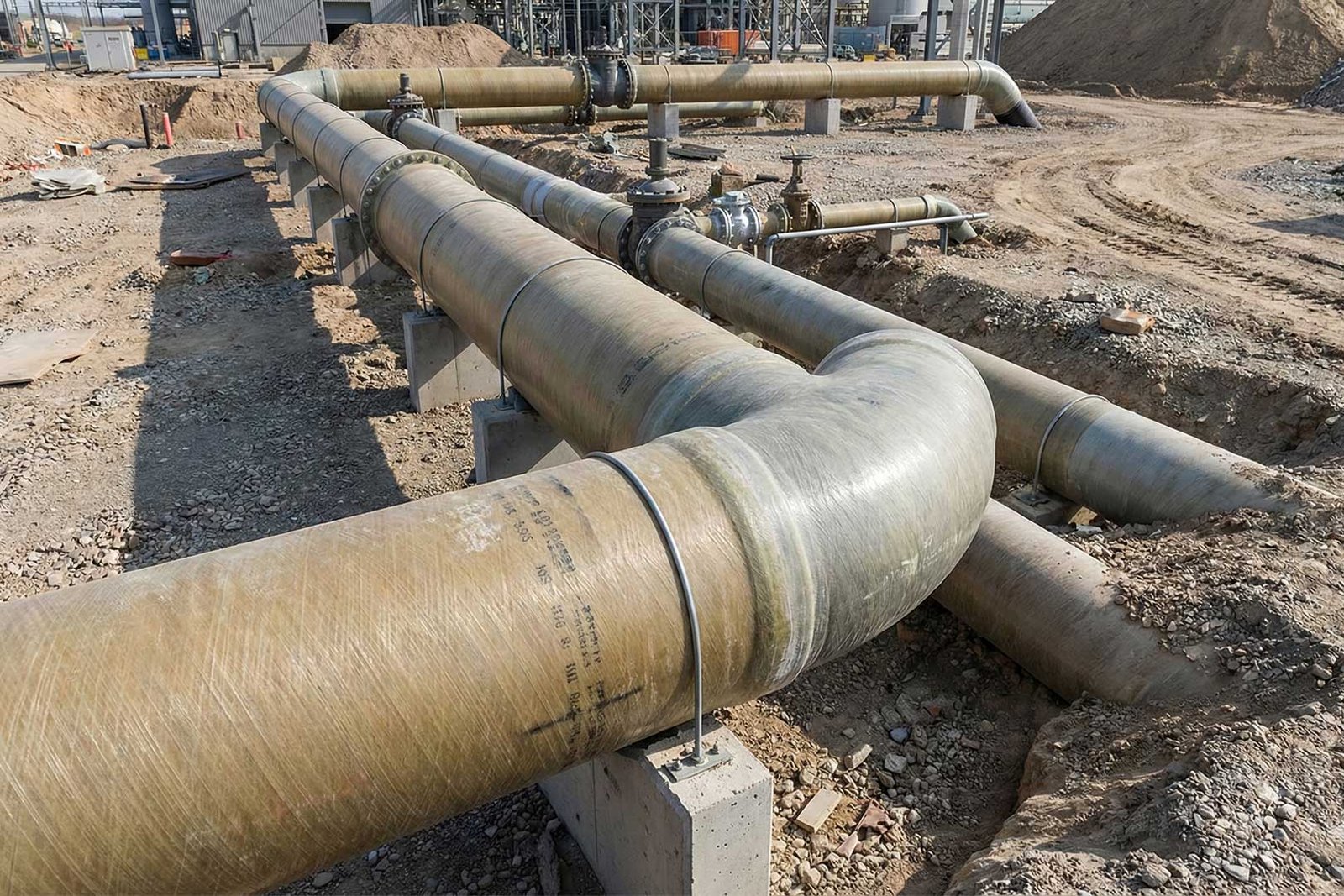
Did you know corrosion-free GRP pipes can reduce the maintenance costs and pipe failure over traditional pipes? Explore their exceptional use cases across industries! Glass Reinforced Plastic (GRP) pipes are composite material created from glass fibers and resin matrices (polyester, vinyl ester, and epoxy). This structure made a perfect choice for water, chemicals, and other fluids’ transmission across various industries due to its lightweight, corrosion resistance, and durability.
This guide dives into the GRP pipe’s use cases worldwide through its magnificent specifications to aid engineers, contractors, and project managers for the proper piping system selection.
Before getting into the full explanation of GRP pipe use cases, let’s review them at a glance through this table below:
| Sector | Main Uses | Why GRP Works Best |
|---|---|---|
| Potable Water | Drinking water, distribution lines | Corrosion-free, maintains water quality, low friction loss |
| Wastewater & Sewer | Gravity sewers, pressure mains | Chemically resistant, abrasion-proof, ensures smooth flow |
| Stormwater & Drainage | Urban drainage, culverts | High stiffness, flexible under load, resists soil pressure |
| Industrial & Chemical | Acid/alkali transport, effluent pipelines | Withstands aggressive chemicals and heat, no metal corrosion |
| Cooling & Power Plants | Cooling circuits, discharge pipelines | Insulates heat/electricity, durable in continuous flow systems |
| Marine & Desalination | Saltwater intake, ballast systems | Anti-fouling, lightweight, handles high salinity environments |
| Oil & Gas | Crude oil, gas injection, offshore piping | API-compliant, pressure-resistant, cost-effective in harsh zones |
| Irrigation & Agriculture | Field networks, canal lining | UV-resistant, leak-proof, minimal maintenance and cost |
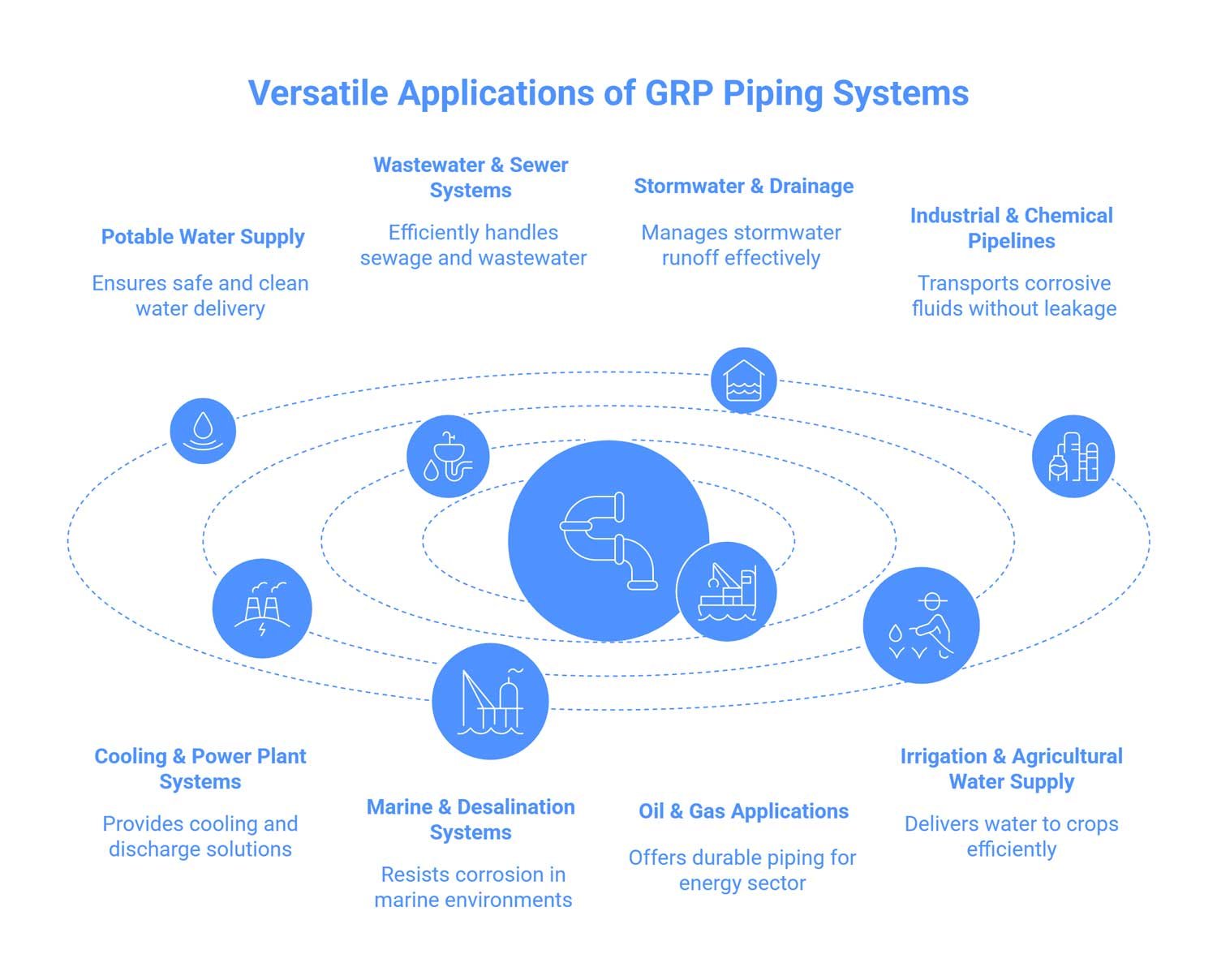
The 8 Most Common Uses of GRP Piping Systems
GRP pipes are top choices in modern projects over traditional pipelines like steel or concrete. This composite combination of fiberglass and resin systems provides a wide range of fruitful properties for various applications. Below, we’ll explain the most commonly used use cases of GRP pipes:
1. Potable Water Supply
For an easy, safe, and clean water delivery followed by international standards, GRP pipes are used for water supply due to their non-corrosive nature and high strength-to-weight ratio. Main applications include:
Drinking Water Mains: To prevent contamination and keep the water quality at the highest range all over long pipe distances, GRP pipes with smooth and corrosion-resistant inner surface play a long-lasting performance in drinking water transmission.
Distribution and Transmission Pipelines: For high-pressure flows with low head loss, GRP pipes are ideally used in both large- and small-scale water systems.
- Technical Insight: For potable water systems, GRP pipes are manufactured and evaluated by standards like AWWA C950 or ISO 10639 to handle high-pressure systems with no leak or deformation.
2. Wastewater & Sewer Systems
GRP pipes effectively resist chemicals and complex fluids like wastewater and harsh sewage conditions. Applications are:
Gravity sewer refers to the efficient sewage handling via smooth bore with no blockage or speed reduction.
Pressure/rising pipes that endure high-pressure flows to transfer sewage over long distances or elevations.
Industrial effluent discharge goes through managing the highly corrosive wastewater with no degradation over the years.
- Real-World Example: For instance, in Slovakia, 640 meters of GRP pipes replaced corroded steel pipes for high groundwater levels and heavy traffic tolerance due to the durability and corrosion resistance of GRP pipes.
3. Stormwater & Drainage
In urban and rural piping systems, stormwater management relies on GRP pipes due to their durability and high flow capacity. Most-used applications include:
Urban Drainage Systems: Flood prevention through efficient runoff channel designing in cities.
Culverts and Rainwater Channels: GRP pipes used in this case due to high external load tolerance in aggressive soils with minimum maintenance needs.
- Insight for Engineers: The special design of GRP pipe allows them to resist under high pressures up to 10 kN/m2 based on the stiffness class (SN 200-10,000). (Source: Amiblu)
4. Industrial & Chemical Pipelines
In chemical plants and industrial transmissions for acids, alkalis, or other corrosive solvents, unlike corroded pipelines like steel or concrete, GRP pipe provides a reliable piping system with no leakage. Applications contain:
Acid and Alkali Handling: The resin choice can differ to meet the project’s demand. For instance, vinyl ester resists specific chemicals like sulfuric acid or sodium hydroxide.
Corrosive Fluid Transmission: In addition to the chemical transmission, aggressive environments require protective layers, while GRP pipes need no extra coating added.
- Technical Tip: Via adding specific resin bases like vinyl ester or epoxy, FRP pipes can tolerate high temperatures up to 120-150°C.
5. Cooling & Power Plant Systems
GRP pipes are perfect for power plants due to their non-conductive nature and corrosion resistance.
Cooling water systems: With lightweight yet strength of GRP pipes, they’re normally used in cooling towers to reduce the thermal expansion.
Effluent and Discharge Pipelines: GRP pipes avoid corrosion in treated water discharge via resin coating and lining.
- Pro Tip: The low thermal conductivity of GRP pipes (≈0.3 W/m·K) compared to steel (≈50 W/m·K) and UV-resistant coating makes them perfect for above-ground installations while decreasing the heat loss.
6. Marine & Desalination Systems
The corrosion threat of desalination and marine environments makes GRP pipe a superior choice with no damage from biofouling or saltwater corrosion. Applications include:
Saltwater Intake and Outfall: Used in desalination plants with high water flow tolerance.
Ballast Cooling Lines: to resist in harsh marine and offshore platforms where vessels require strong and non-corrosive pipelines.
- Additional Point: The smooth inner surface of GRP pipes is designed for biofouling reduction and high-pressure flow tolerance up to 16 bar for seawater systems.
7. Oil & Gas Applications
GRP pipes shine in the energy sector where offshore oil platforms require easy and cost-effective pipelines that resist corrosion from hydrocarbons and produced water.
Offshore Platform Piping: In remote locations, lightweight and easy installation and jointing matter the most.
Oil and Gas Pipelines: For crude oil, gas injection, and produced water pipelines, GRP pipes tolerate aggressive fluids with no degradation.
According to Shejiyuan, GRP pipes for oil and gas are designed to API 15HR standards, handling pressures up to 40 bar and temperatures up to 100°C, depending on resin type. Their fatigue resistance ensures reliability in cyclic loading conditions.
8. Irrigation & Agricultural Water Supply
In irrigation and agricultural supply systems where UV light and harsh soils require pipes with resistance to corrosion and durability in seismic zones, GRP pipes provide durable performance over decades.
For instance, in field distribution systems, they transform water to crops with no leaks, while in canal liners, they show a reliable water transportation for irrigation networks.
- Technical Insight: GRP pipes for irrigation are designed with lower stiffness classes (SN 2500-5000) for cost efficiency in low-pressure systems. Also, their smooth inner surface decreases pumping costs, and UV-resistant coatings protect against prolonged exposure to the sun.
Application-Specific Advantages of GRP Pipes
As we mentioned in the last section, GRP pipes include several beneficial properties for diverse use cases from irrigation to offshore platforms. Here are some of these magnificent characteristics:
Resistance to Biofouling in Marine/Desalination Use
The smooth inner surface of GRP pipes that comes from resin layers reduces biofouling and maintenance cost up to 50% in saltwater systems.
Chemical Stability in Industrial Settings
GRP industrial piping can be designed by vinyl ester or epoxy resins for improving the tolerance in high temperatures over traditional pipes that provide galvanic corrosion.
Pressure Handling in Oil/Gas and Hydropower
GRP pipes handle pressures up to 40 bar (API 15HR), and unlike heavy steel pipes can resist cyclic loads and high-pressure systems.
Smooth Flow in Sewage and Stormwater Systems
ResearchGate highlights that via their smooth inner surface, GRP pipes include a low roughness (Hazen-Williams C ≈ 150) that reduces the need for maintenance and pumping costs by 10-15%.
| Application | GRP Pipe Benefit | Compared to Traditional Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Marine & Desalination | Anti-biofouling, corrosion-free | Steel pipes clog and corrode in saltwater |
| Industrial & Chemical | Chemical stability, no galvanic corrosion | Metal pipes degrade with acids/alkalis, require frequent replacement |
| Oil/Gas & Hydropower | High pressure/fatigue resistance, lightweight | Steel heavier, less durable under cyclic loads |
| Sewage & Stormwater | Smooth flow, abrasion-resistant | Concrete pipes rougher, prone to sediment buildup |
Summary: Matching GRP Pipes to the Right Use Case
GRP pipes are durable and lightweight pipelines for modern piping infrastructures. Selection of GRP pipes eases the process of transportation and installation, while providing over 50 years of performance under heavy loads and harsh conditions.
How to choose the right GRP pipeline for your project?
Consider aspects below to select the best pipeline for your piping systems:
- Environmental Considerations: Match resins (e.g., vinyl ester for chemical resistance, epoxy for high temperatures) to corrosive soils, seawater, or chemicals.
- Pressure and Temperature: design pipes based on the required pressure ratings, for instance, up to 40 bar (API 15HR) and 120°C for applications like GRP oil and gas pipes or power plants.
- Installation Method: GRP pipeline installation provides various methods like open trench, trenchless, above-ground, or underwater for projects like GRP sewer pipes or GRP marine pipes.
- Lifecycle Costs: Leverage 50–100-year lifespans and low maintenance for cost savings in GRP pipes for water supply or GRP drainage pipes.
- Standards Compliance: GRP pipes are certified by guidelines like AWWA C950 or ISO 10639 for long-term performance, where repairing and maintenance are difficult.
Performance Comparison: GRP Pipes vs. Traditional Piping
Recent trends of piping systems follow sustainable and long-lasting pipelines like GRP pipes. Unlike alternative pipes such as steel or concrete, GRP pipes win the projects due to their corrosion resistance, lifecycle cost, and lightweight. The table below shows these differences more vividly:
| Criteria | GRP vs. Steel | GRP vs. Concrete | GRP vs. Ductile Iron |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Superior | Superior | Superior |
| Weight & Handling | Lighter | Much lighter | Lighter |
| Installation Speed | Faster | Faster | Faster |
| Maintenance Costs | Lower | Lower | Lower |
| Service Life (Years) | 50+ vs. 15-20 | 50+ vs. 30–40 | 50+ vs. 25–40 |
What Are the Popular Industries and Infrastructure Sectors Using GRP?
GRP pipes are top choices for various industrial and rural projects due to their durability, corrosion resistance, and tolerance in high-pressure and temperature conditions. Here are some of the most-used sectors of GRP pipes:
- Water and Wastewater: Potable water supply, gravity sewers, effluent discharge.
- Oil and Gas: Crude oil, gas injection, offshore platform piping.
- Chemical Processing: Acid and alkali transmission.
- Power Generation: Cooling water circulation, effluent pipelines.
- Marine and Desalination: Saltwater intake/outfall.
- Agriculture: Irrigation and water supply.
Final Tip
To select the best and proper GRP pipe system for your project, consult with suppliers or GRP manufacturers to design the pipeline’s specifications such as resin type, pressure class, and joint systems based on the project’s demand. Consider that a well-designed GRP pipeline will reduce the need for further maintenance, while lasting at least 50 years.
FAQs
1- What are GRP pipes used for in potable water supply?
GRP pipes are used for water supply due to their non-corrosive nature and high strength-to-weight ratio, including drinking water mains and distribution pipelines.
2- Why are GRP pipes effective for wastewater systems?
GRP pipes resist chemicals in wastewater, used in gravity sewers, pressure mains, and industrial effluent discharge with no degradation.
3- How do GRP pipes perform in marine environments?
GRP pipes resist biofouling and saltwater corrosion in desalination plants and ballast cooling lines.
about
The Author
Farshid Tavakoli is a seasoned professional in engineering and international trade. Holding degrees in Electrical Engineering, Mechatronics, and a Doctorate in Business Administration (DBA) from the University of Lyon, he also has a strong background in industrial automation and production line technologies.
For over 17 years, he has led an international trading company, gaining deep expertise in commercial solutions tailored to industrial needs. With more than 8 years of active involvement in infrastructure development, he specializes in the supply of electromechanical equipment for water and wastewater treatment plants and transfer projects.
Together with comapny expert team, he now provides consultancy and integrated solutions for sourcing and implementing complex infrastructure projects across the region.